Research
Funds
- 国家外国专家个人类项目(H类),人机共融助行外骨骼机器人关键理论和技术研究,2025.01至2026.12,20万,主持
- 人体姿态感知信息度量自适应估计理论及应用,国家自然科学基金青年科学基金,2025-01至2027-12,30万元,主持
- 某软件测试项目,北京空间飞行器总体设计部,2024-06至2025-06,60万元,主持
- 面向空间机械臂的智能持续生长技术开发,北京控制工程研究所,2025-08至2026-08,8万元,主持
- 面向可穿戴无创生理监测的主动采样感知与状态估计研究,北京市自然科学基金-北京杰青项目,2024-07至2027-06,100万元,参与
- 面向手机直连应用的高低轨卫星协同处理平台开发技术,中国空间技术研究院,2024-09至2025-09,75万元,参与
- A Synergetic Human-Machine Exoskeleton System for Walking Assistance of Stroke Patients in ADLs, Innovation and Technology Commission, Hong Kong, 2019-09至2021-08, HK$4516800, main participants.
Research Interests
- Statistical Learning, Multi-sensor Information Fusion
- Exoskeleton Robot, Humanoid Robot
- Human-Machine Symbiosis
Research Experience
1. Robust State Estimation
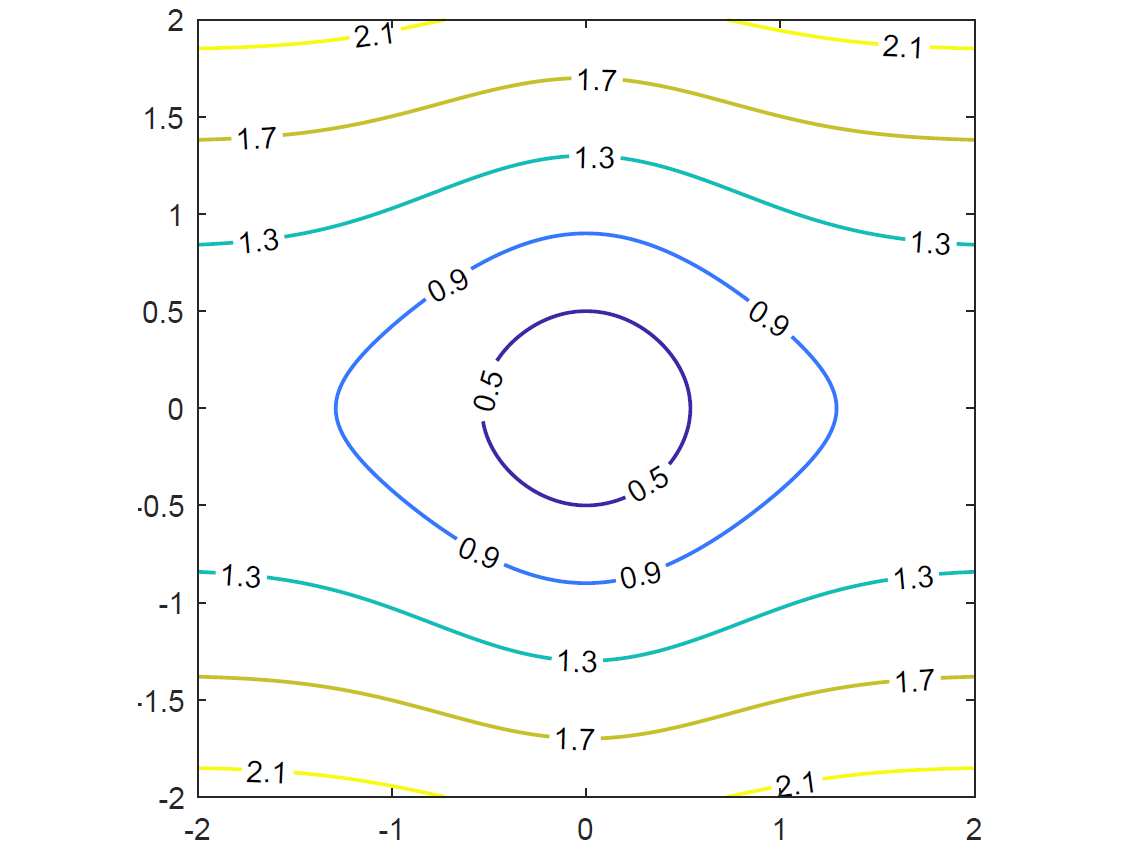 |
The well-known mean squared error (MSE) based algorithms are sensitive to outliers or non-Gaussian noise.
To handle this issue, we propose a novel metric which is called multi-kernel correntropy and derive some robust estimators. Relevant works:
|
2. Orientation Estimation of IMUs
 |
Inertial measurement units are widely used in the field of gait assessment, human-robot interaction, motion animation,
and virtual and augmented reality. However, their performances are greatly affected by external acceleration and magnetic disturbance. To cope with this issue, we employ
the multi-kernel correntropy to replace the mean squared error (MSE) based cost function, and derive some robust orientation estimation estimators for IMUs. Relevant works:
|
3. Preference-based control for light-weight exoskeletons
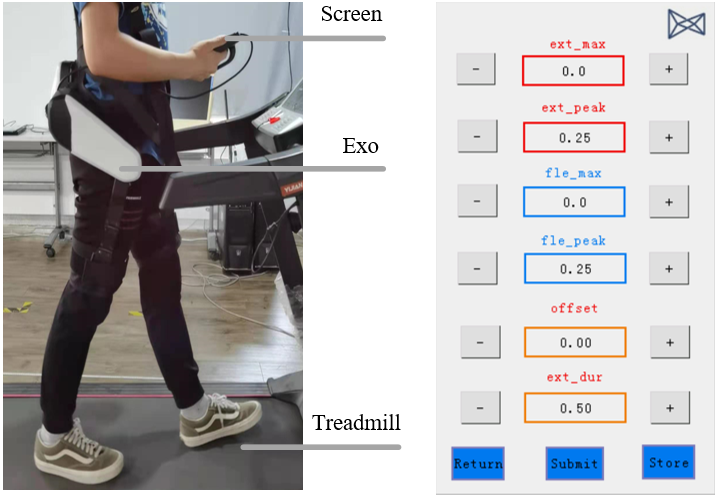 |
To provide the individualized assistance profile for walking in a community, we provide
a preference-based learning scheme for walking assistance in a community. Relevant work:
|
4. Strength augmentation using exoskeletons
 |
We propose a mixed-control scheme for strength augmentation using exoskeletons. The exoskeleton can carry
a heavy load and follow the user's different walking modes, e.g., level walking, stair ascend, and stair descent. Relevant work:
|